Routine and special histochemical stains
Hematoxylin and eosin stain
One of the principal stains in histology and pathology. Considered the standard for most routine diagnostic pathology, it serves as the primary stain in diagnostics and research, especially for preliminary evaluation. Staining pattern:
- Mitochondria in pale pink
- Collagen in pale pink
- Erythrocytes in cherry red
- Muscles in dark red
- Cytoplasm in red
- Basophils in purplish red
- Nuclei in blue/purple

Masson’s trichrome stain
A three-color staining protocol, usually for distinguishing cells from surrounding connective tissue. Staining pattern:
- Keratin and muscle fibers in red
- Collagen and bone in blue or green
- Cytoplasm in light red or pink
- Cell nuclei in dark brown to black
Phosphotungstic acid hematoxylin stain (PTAH)
A variant of trichrome stain; demonstrates intracytoplasmic filaments in muscle and glial cells. Staining pattern:
- Muscles in blue-black to dark brown
- Connective tissue in pale orange-pink to brownish red
- Fibrin and neuroglia in deep blue
- Coarse elastic fibers in purple
- Bone and cartilage in yellowish to brownish red
Gram staining
A common microbiologic stain used to differentiate two large classes of bacteria based on the difference in their cell wall composition.
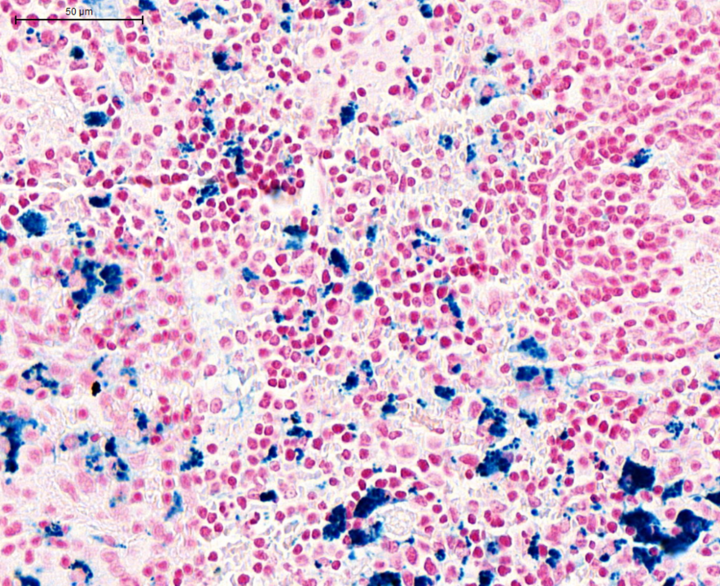
Prussian blue
A staining method used to detect the presence of iron

Alcian blue
A method used to stain acidic polysaccharides such as glycosaminoglycans in cartilage and other body structures

Oil red O
A fat soluble dye used to stain triglycerides and neutral lipids bright red
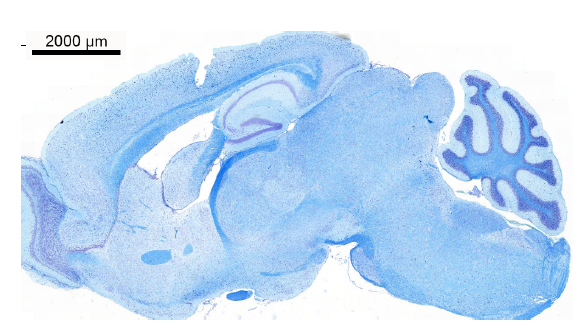
Luxol Fast Blue–Cresyl Violet
A two-component staining method that enables identification of neuronal Nissl substance and axonal myelin in nervous tissue.
Toluidine blue
A dye with high affinity for acidic tissue components. It stains nucleic acids blue and polysaccharides purple thus enabling metachromatic staining of certain types of cells and tissue components (e.g. Mast cells).

Gomori’s methenamine stain
Used widely as a screen for fungal organisms. Particularly useful for staining carbohydrates.

Reticulin stain
A staining method used to demonstrate reticular (retic) fibers

Von Kossa stain
A stain used for visualization of calcium deposits
Bodian stain
This method uses silver proteinate, copper, and gold chloride to stain neuronal cell bodies (soma) and nerve processes dark brown. Fiber components in normal structures and neuropathologic lesions are stained. Examples include areas of localized axonal swelling (spheroids), dendritic lesions, and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) in Alzheimer’s neurodegeneration.

May-Grunwald Giemsa stain
This stain is used in hematology to differentiate and count different blood cell populations in cellular preparations (cytology).

Benzidine staining
This method is used to stain the hemoglobin of erythrocytes dark brown.

Feulgen stain
This is one of the techniques used to visualize nuclear chromatin and is often used to perform semiquantitative assessment of DNA .